What is the structure of the nucleic acids
Nucleic acids, deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA), carry genetic information which is read in cells to make the RNA and proteins by which living thing function. The well-known structure of the DNA double helix allows this information to be copied and passed on to the next generation.
What is DNA?
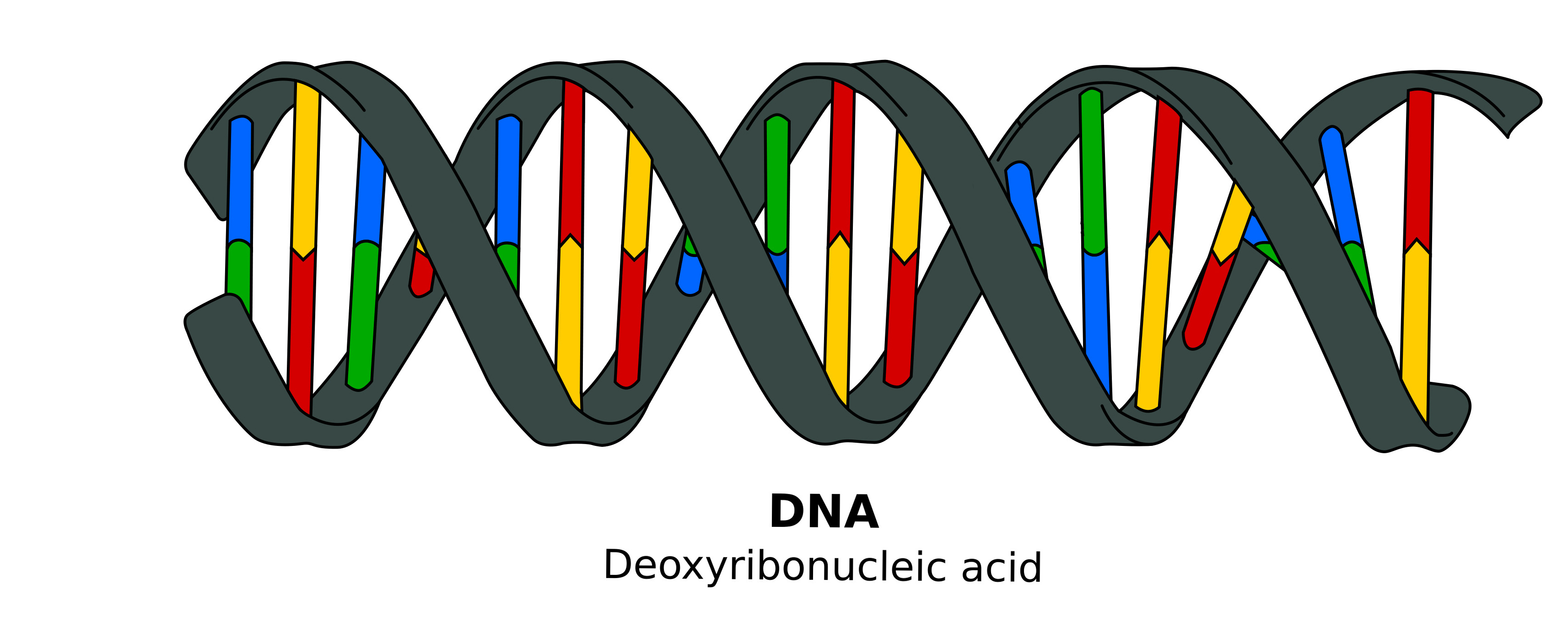
DNA is a polymer made of monomeric units called nucleotides, a nucleotide comprises a 5-carbon sugar, deoxyribose, a nitrogenous base and one or more phosphate groups. The building blocks for DNA synthesis contain three phosphate groups, two are lost during this process, so the DNA strand contains one phosphate group per nucleotide.
There are four different bases in DNA, the double-ring purine bases: adenine and guanine; and the single-ring pyrimidine bases: cytosine and thymine (Figure 1B). The carbon within the deoxyribose ring are numbered 1 to 5. Within each monomer the phosphate is linked to the 5 carbon of deoxyribose and the nitrogenous base is linked to the 1 carbon, this is called an N-glyosidic bond. The phosphate group is acidic, hence the name nucleic acid. In the DNA chain (Figure 1B), the phosphate residue forms a link between the 3-hydroxyl of one deoxyribose and the 5-hydroxyl of the next. This linkage is called a phosphodiester bond. DNA strands have a ‘sense of direction’. The deoxyribose at the top of the diagram in Figure 1B is not linked to another deoxyribose; it terminates with a 5 phosphate group. At the other end the chain terminates with a 3 hydroxyl.
What is RNA?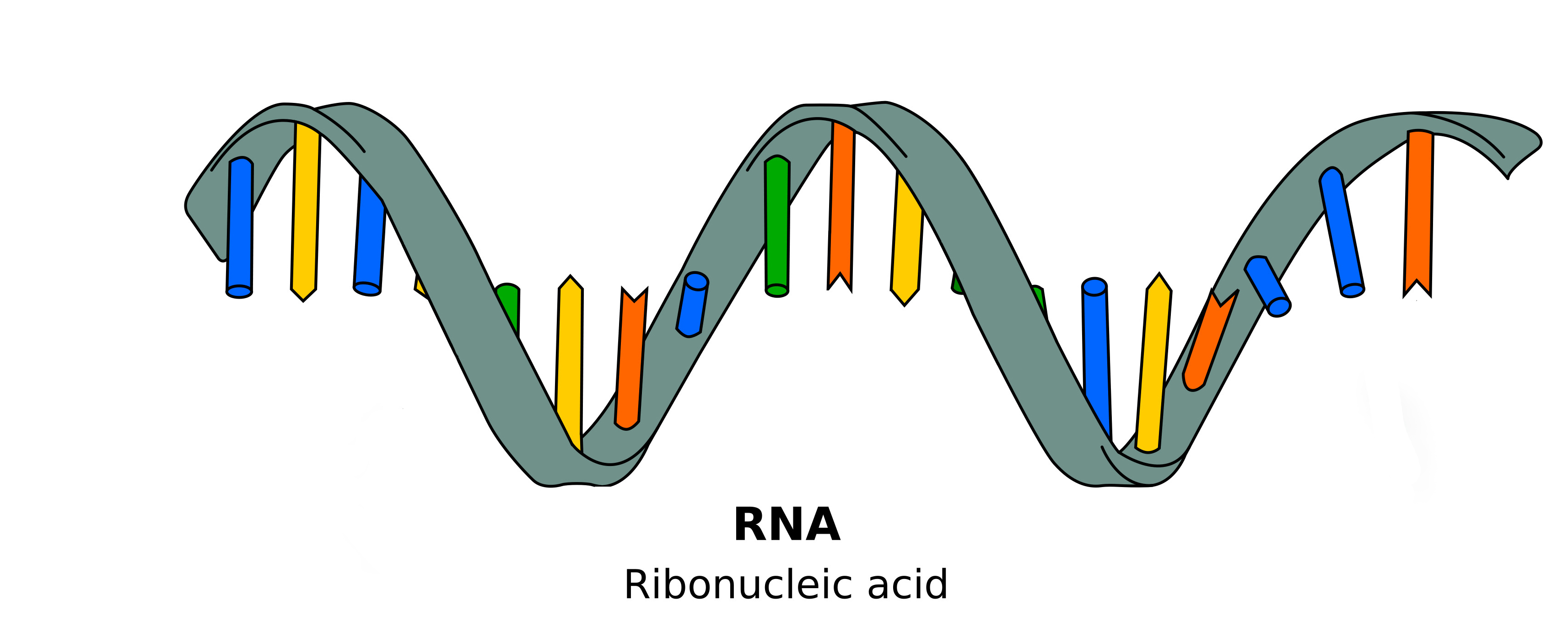
Another important class of nucleic acids is RNA, the roles of RNA molecules in the cell will be discussed below. Chemically RNA is similar to DNA, it is a chain of similar monomers. The building blocks are nucleotides containing the 5-carbon sugar ribose, a phosphate and a nitrogenous base. The phosphate is attached to the 5 carbon of the ribose and the nitrogenous base to the 1carbon. RNA contains four bases adenine, guanine, cytosine and uracil. RNA is more labile (easily broken down) than DNA and most RNA molecules do not form stable secondary structures, some notable exceptions will be discussed below. The properties of RNA make it ideal as a genetic messenger during protein synthesis, the idea of this genetic messenger, mRNA, was proposed by Francois Jacob and Jacques Monod.
Nuclear organization plays an important role in many biological processes including regulation of gene transcription. In recent years the development of several techniques, including microscopy, have allowed us to gain an understanding of the way the genome is organized in 3D. Individual chromosomes are not randomly spaced within the nucleus; each chromosome has a distinct territory. Actively transcribed regions from different chromosomes are often close to each other and near the interior of the nucleus, whereas, inactive genes are on the periphery or near a special area called the nucleolus where ribosomal RNA is transcribed.
Geneture Medical, provides one stop solution of Nucleic Acid Extraction and Analysis. If you need more information about nucleic acid , please feel free to contact.
- SKU: Jack
- Category: News
Additional Information
Send an Inquiry
Your email address will not published. Required fieled are marked.
Related Products
Check out other related DNA/RNA Extraction Products
